Corona
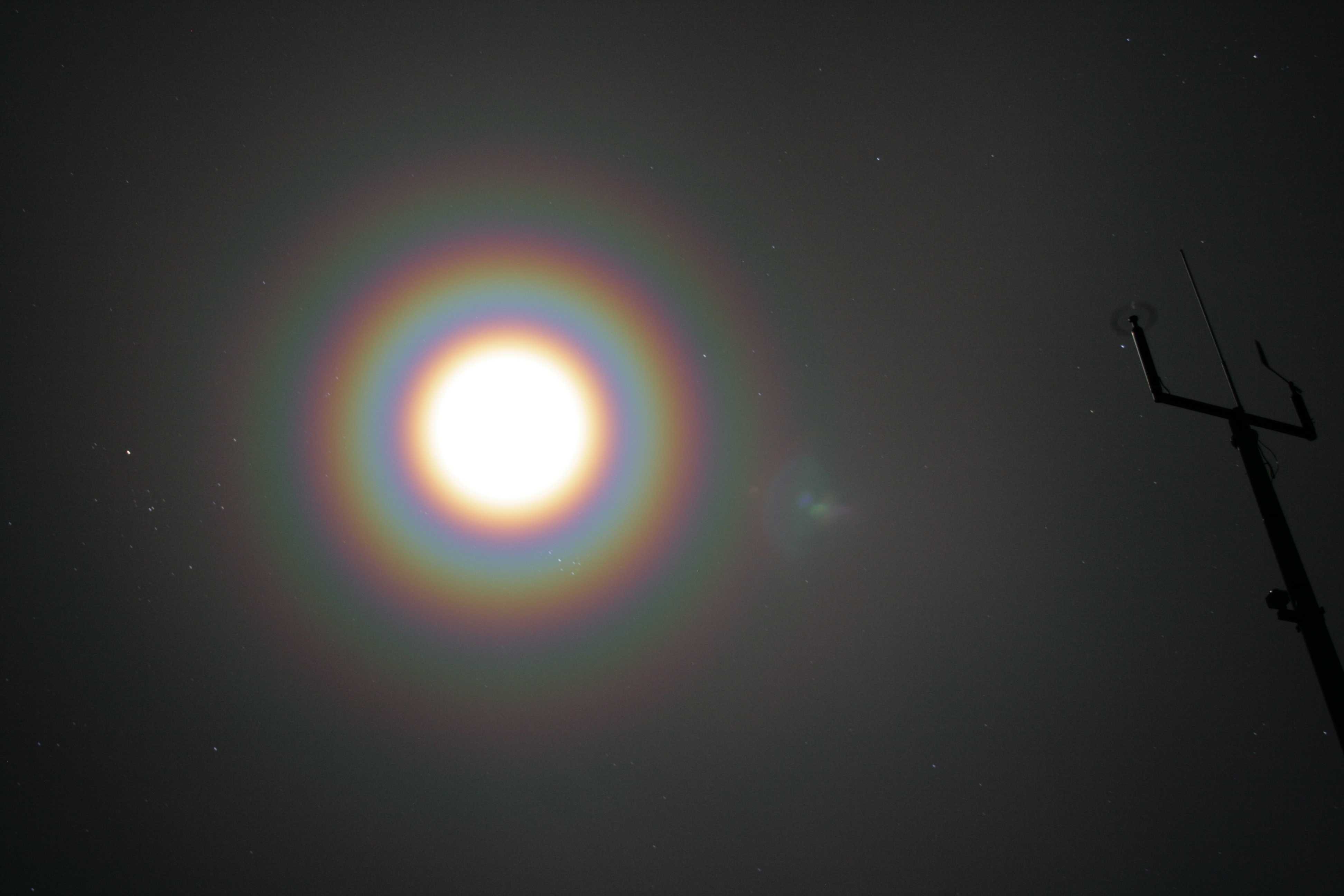
(Section 3.2.3.2)Definition: Corona: One or more sequences (seldom more than three) of small-diameter coloured rings centred on the Sun or Moon.
In each sequence, the inside ring is violet or blue, the outside ring is red and other colours such as green and yellow may occur in between. The innermost sequence, which is generally not more than 5° in diameter, usually has a central area that is intensely bright, and a distinct outer ring of reddish or chestnut colour, called the “aureole”.
Coronae are caused by the diffraction of light from the light source (Sun or Moon), passing through mist, fog or thin cloud composed of very small water or ice particles. Coronae may also occur when light is diffracted by large amounts of pollen in the air. The radii of the aureole and of the successive, approximately equidistant, red rings are greater for smaller particles. When the particles are not uniform in size, the colours observed in coronae are less pure and fewer than the colours of the rainbow.
Sometimes, coronae seen in clouds appear distorted because of particle size differences in various parts of the clouds. Distorted coronae with small radii may also be observed around the Moon because, except when full, the Moon is not a symmetric light source. The corona can be as much as 15° in diameter, and may shrink or swell as different clouds pass across the Sun or Moon.