Hydrometeors consisting of a vortex of particles (Spouts)
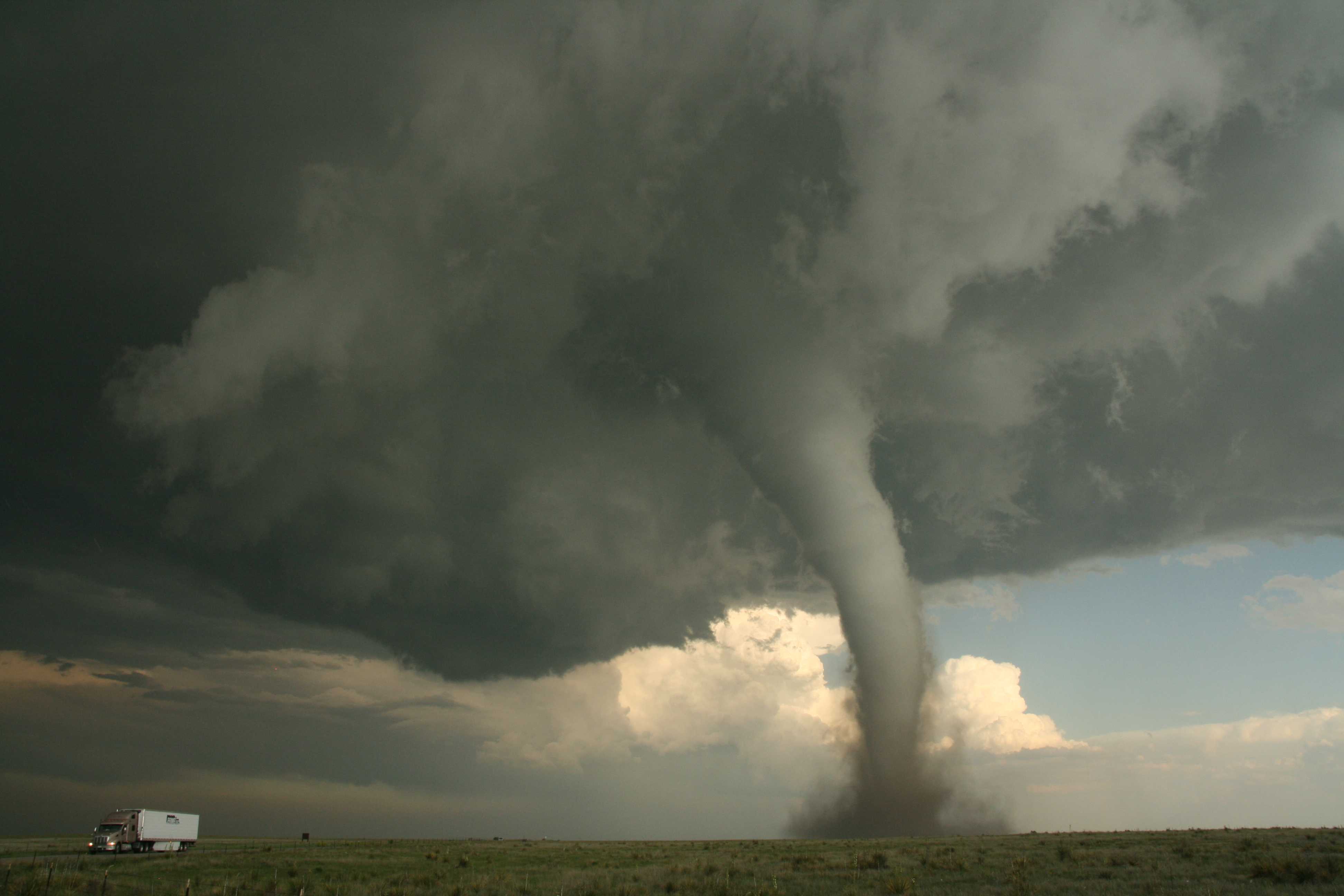
(Section 3.2.1.5)Definition: Spout: A phenomenon consisting of an often violent whirlwind, revealed by the presence of a cloud column or inverted cloud cone (funnel cloud), protruding from the base of a Cumulonimbus or Cumulus cloud, and of a “bush” composed of water droplets raised from the surface of the sea or of dust, sand or litter raised from the ground.
The axis of the funnel cloud is vertical, inclined or sometimes sinuous. Sometimes, the funnel merges with the bush. The air in the whirlwind, or vortex, rotates rapidly, most often in a cyclonic sense. Rapid rotation may also be observed outside the funnel and the “bush”. Further away, the air is often very calm. The diameter of the cloud column, which is normally of the order of 10 m, may occasionally reach some hundreds of metres. Several spouts (multiple vortices) may sometimes be observed connected with a single cloud. Some spouts (tornadoes) can be extremely destructive, where they may leave a path of devastation up to 5 km wide and several hundred kilometres long. Weak spouts are occasionally observed under Cumulus clouds.
Spouts can be divided into four categories.